Raspberry can control Motor and Servo with the help of its various expansion helpers.
The main difference betwen DC motor and servo is that motor will only have 2 wires: positive (red) and ground (black), whereas servo have 3 wires: positive (red), negative (black), and signal (white).
There are a few good boards that are specifically designed to work for Raspberry, such as: PiFace, Raspy Juice and Gertboards, but there are also other available such as Pololu, Romeo, Dagu, and the Arduino boards.
Here are a few examples that provem to work with the Raspberry Pi:
PiFace
- Controls 2 motors and 1 servo
- Interfaces: GPIO, 8 buffered input pins (with 4 switches on-board connected to 4 of these pins), and 8 buffered output connections. 2 of the output connections are connected to mechanical relays, 4 buttons and 4 LEDs
- Supported language: Python, C
- Additional features: nice slim design can piggy-back nicely on the Pi
- Limitation: enclosed GPIO port
- Controls 4 servos, and no motor
- Interfaces: GPIO, RS232, RS485
- Supported language: Python, C
- Supported protocol: I2C, Atmel ATmega168A AVR microcontroller
- Additional feature: power port that is enough to supply for Raspberry Pi
- Limitation: cannot work with pre-powered Remote Control Car, e.g. those that work with the engine, although the steering works Ok
Gertboard
- Controls 1 motor, 1 servo, and possibly 1 more servo through relay
- Interfaces: GPIO (direct access to pins), relays, buffers, native motor port.
- Supporte language: Python, C
- Supported protocol, Atmel ATmega256 AVR microcontroller
- Additional features: LEDs, and power choices of 3.3v or 5 v.
- Limitation: size larger than Pi, and has to be piggy bagged on the side.
Other components that are not specifically designed for Raspberry Pi
- Controls 6 servos
- Interfaces: Analog, digital, USB, 6 servo ports
- Supported language: Mono, C#, Python
- Supported protocol: Directly via serial port, or Maestro Control Centre
- Additional features: ESC, size is small as big as a coin
- Limitation: Does not support motor control
Cooking Hacks Raspberry to Arduino Bridge
- Controls various Arduino servo and motor boards
- Interfaces: i2C, SPI, UART, analog, digital
- Supported language: Arduino IDE scripts
- Supported protocol, various
- Additional features: Sits nicely on the Pi’s GPIO
- Limitation: No native motor or servo ports, requires additional Arduiono board.
4 Channel DC Motor Controller with Encoder Support
- Controls 4 motors natively, no servos support
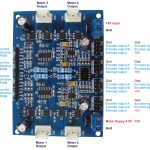
- Interfaces: 4 2-pins motor ports, 2 power ports, encoders, and PWMs
- Supported language: Unknown
- Supported protocol: PWM, encoders
- Additional features: low cost 4 channel motor controllers
- Limitation: No direct interfacing for Raspberry Pi, can be done via Arduino shield
- Additional features: Sits nicely on the Pi’s GPIO
- Limitation: No native motor or servo ports, requires additional Arduino board.
Other awesome board: Romeo V2
Romeo V2 All in One Motor Controller is a micro controller on its own right rather than a Raspberry Pi expansion. This little black board made by DFRobot is capable of storing and running Arduino Sketches, getting commands via TX and RX pins as well as MicroUSB.
[post_view]
5 thoughts on “Raspberry Pi Motor and Servo Controller Expansion boards”
Comments are closed.






How did you get the raspberry pi to control the maestro board, Mine hangs at read()
I open the device using open(“/dev/ttyACM0”);
I then write the command to get Target using write();
when I run read(); the board hangs.
Event when I try cat /dev/ttyACM0 nothing?
Did you have similar issues?
How did you try to read, and what did you try to read? You have to find the right port for your usb device using the command dmesg.
Were you able to write?
Yes my write succeeds, I am opening and writing to /dev/ttyACM0 using C. and /dev/ttyACM0 corresponds correctly to my dmesg output. Did you work straight from the outset?
If so could I ask you to try the following code https://code.google.com/p/androneee/source/browse/trunk/playground/src/helloworld.cpp It will read error, get and set the position.
The above code works on my laptop fine just not on the Pi. And I am not sure how you are using your pi to communicate to the board
If it works on laptop but not the Pi, the problem maybe because it does not have the Serial library
Thanks for posting this, super helpful!